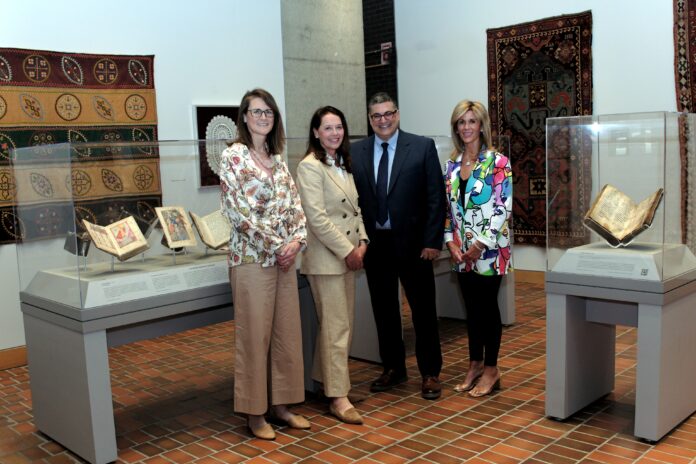
BOSTON — As part of its Art Conservation Project, Bank of America provided a grant to the Armenian Museum of America of Watertown to restore 21 illuminated manuscripts from its collection, one of which dates back to the 13th century, the museum announced this week. Bank of America selected the Armenian Museum of America as one of the 23 cultural institutions that have been named recipients of the 2023 Bank of America Art Conservation Project, a program that provides grants to nonprofit cultural institutions to conserve important works of art.
This year’s recipients represent a diverse range of artistic styles, media, and cultural traditions across China, Colombia, France, Lebanon, Mexico, Singapore, South Africa, Sweden, the U.K. and the U.S.
The Armenian Museum of America has the largest collection of Armenian artifacts in the United States. Among them is an extremely rare collection of 21 handwritten and hand-illuminated manuscripts, of which approximately 10 are on display in the museum’s galleries at any given time. One example is a small hymnal, or sharaknots in Armenian, which contains hymns to be chanted and performed on feast days. Attributed to the prolific artist Karapet of Berkri, the illumination depicts the Presentation of Christ in the Temple.
Since 2010, Bank of America’s Art Conservation Project has supported the preservation of paintings, sculptures, and archeological and architectural pieces of critical importance to cultural heritage and the history of art. More than 237 projects across 40 countries managed by nonprofit cultural institutions received funding to conserve historically or culturally significant works of art that are in danger of deterioration.
“We are incredibly grateful to Bank of America for providing us with this grant so our manuscripts will be preserved so that they can be viewed by the public and studied in perpetuity without risk of further damage. This partnership will allow visitors to view the art and culture of the past, and to see it in the context of the present in our galleries,” said Jason Sohigian, executive director of the Armenian Museum.
“By the medieval period, Armenians had a rich literary society. Since then, many manuscripts and illuminations have been looted or destroyed, a process that intensified during the Armenian Genocide of 1915. Preservation has taken on a renewed importance, as Armenia’s cultural heritage remains at risk,” he added.