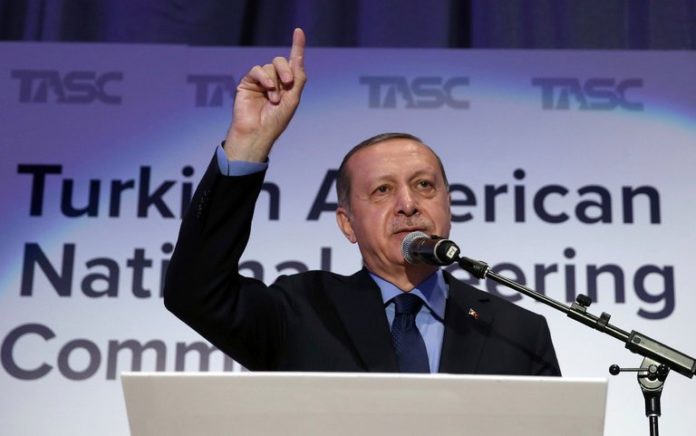
ANKARA (Reuters) — Turkish President Tayyip Erdogan won sweeping new executive powers on Monday, June 25, after his victory in elections that also saw his Islamist-rooted AK Party and its nationalist allies secure a majority in parliament.
Erdogan’s main rival, Muharrem Ince of the Republican People’s Party (CHP), conceded defeat but branded the elections unjust and said the presidential system that now takes effect was “very dangerous” because it would lead to one-man rule.
A European rights watchdog also said the opposition had faced “unequal conditions”, adding that restrictions on media freedom to cover the elections were accentuated by a continuing state of emergency imposed in Turkey after a failed 2016 coup.
Erdogan, 64, the most popular — yet divisive — leader in modern Turkish history, told jubilant, flag-waving supporters there would be no retreat from his drive to transform Turkey, a NATO member and, at least nominally, a candidate to join the European Union.
He is loved by millions of devoutly Muslim working class Turks for delivering years of stellar economic growth and overseeing the construction of roads, bridges, airports, hospitals and schools.
But his critics, including rights groups, accuse him of destroying the independence of the courts and press freedoms. A crackdown launched after the coup has seen 160,000 people detained, and the state of emergency allows Erdogan to bypass parliament with decrees. He says it will be lifted soon.